The Evolution of Bagasse Tableware Machine: From Manual to Automated Production
- june11433
- Nov 12, 2024
- 3 min read
The push for sustainable alternatives in the packaging and foodservice industries has led to a surge in demand for biodegradable products. As a result, bagasse—an eco-friendly byproduct derived from sugarcane waste—has gained popularity for its ability to produce disposable, yet compostable, tableware. Central to this shift is the development of the bagasse tableware machine, which has evolved dramatically over the years. This progression from manual to fully automated production lines is revolutionizing how sustainable products are manufactured.
The Early Days: Manual Production Techniques
In its earliest stages, the production of bagasse-based tableware relied heavily on manual labor. The initial process involved converting raw bagasse fibers into pulp, which would then be manually shaped using basic molds. This method was labor-intensive and inefficient, limiting output to small batches. It was also prone to inconsistencies in quality, with variations in thickness, texture, and durability being common due to the lack of standardized processes.
While these manually operated machines were cost-effective for small-scale producers, they were not viable for large-scale production. As demand for sustainable tableware increased, manufacturers began seeking more efficient methods to scale their operations while maintaining product quality.
The Transition to Semi-Automation
To address the limitations of manual processes, the industry saw a gradual shift toward semi-automated bagasse tableware machine. These machines introduced mechanical components that partially automated the production process, reducing the reliance on manual labor. Key innovations included motorized pulp mixing systems and hydraulic presses, which enhanced the efficiency of molding and reduced human error.
The semi-automated approach allowed manufacturers to increase their output without significantly raising production costs. Additionally, it improved the consistency of the final product, with better control over parameters like pressure and mold temperature. However, these machines still required operators to handle certain aspects, such as feeding raw materials and removing finished products from the molds.
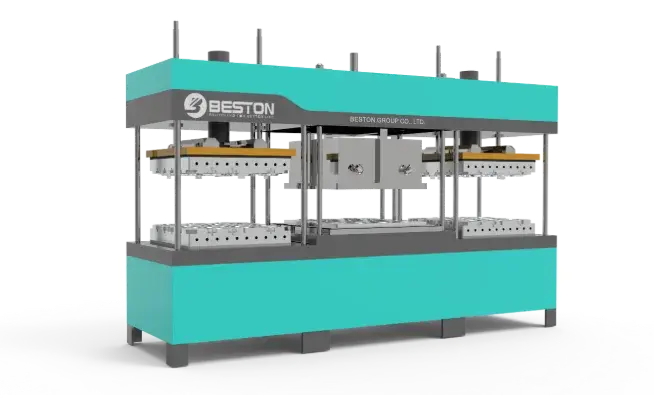
The Era of Full Automation
The most significant leap in the evolution of molded pulp equipment came with the introduction of fully automated systems. These state-of-the-art machines are designed to handle every stage of production, from raw material preparation to final product packaging, without the need for manual intervention. This transition to automation has dramatically improved productivity, making large-scale manufacturing not only feasible but also highly cost-effective.
A modern bagasse tableware machine typically integrates advanced technologies such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), automated pulp feeding systems, and precision molding units. The use of robotics and AI-driven sensors allows these machines to optimize the entire production cycle, ensuring uniform quality while minimizing waste. Automated drying and trimming processes further streamline operations, resulting in faster turnaround times and lower operating costs.
The benefits of automated systems extend beyond efficiency. By eliminating the variability inherent in manual processes, automated machines produce tableware that meets stringent quality and safety standards. This consistency is crucial for companies looking to expand their market reach, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Advantages of Automated Bagasse Tableware Machines
Increased Production CapacityAutomated machines are capable of producing thousands of units per hour, far surpassing the capabilities of their manual counterparts. This scalability is essential for meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly products, especially from large foodservice chains and retailers.
Enhanced Product QualityAutomation ensures precise control over critical production variables, resulting in tableware that is uniform in thickness, strength, and finish. This level of quality control is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Reduced Labor CostsWhile the initial investment in an automated bagasse tableware machine is higher, the reduction in labor costs and increased efficiency quickly offset the expenditure. Additionally, automation minimizes the risk of workplace injuries associated with manual handling.
Sustainability and Environmental ImpactAutomated systems optimize the use of raw materials and energy, leading to lower waste generation. By using bagasse—a renewable, agricultural byproduct—the production process is inherently sustainable, reducing reliance on petroleum-based plastics.
The Future of Bagasse Tableware Manufacturing
As technology continues to advance, the future of bagasse tableware machines looks promising. Innovations in AI, IoT (Internet of Things), and data analytics are expected to further enhance the efficiency of automated production lines. Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and adaptive control systems will likely become standard features, reducing downtime and ensuring maximum output.
Furthermore, as consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there will be an increasing demand for biodegradable products. This will drive manufacturers to adopt the latest automated machinery to stay competitive. In this evolving landscape, investing in cutting-edge bagasse tableware machines is not just an operational choice but a strategic one that aligns with the global push for sustainable development.
Conclusion
The evolution of the bagasse tableware machine reflects the broader trend of integrating automation to meet the needs of a rapidly changing market. From labor-intensive manual methods to fully automated production lines, the journey of this technology highlights the industry's commitment to innovation and sustainability. By embracing these advancements, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, superior quality, and greater sustainability—all essential components in the drive toward a greener future.




Comments